If your child struggles with tic disorders, you’ve likely been told to “just ignore them” or that they’ll “grow out of it.” But what if there’s a more profound connection that most doctors are missing? What if your child’s tics are their body’s way of signaling an underlying histamine dysregulation that can be addressed naturally?
As a functional medicine practitioner who has helped hundreds of families navigate tic disorders, I’ve discovered that histamine imbalances play a crucial role in many cases of childhood tics. It’s more than just a theory; it’s backed by emerging research and real-world results that are transforming our understanding and treatment of tic disorders.
The truth is, conventional medicine often treats tics as isolated neurological quirks, but functional medicine reveals them as symptoms of deeper immune and metabolic imbalances. When we address the root causes—including histamine dysregulation—children can experience remarkable improvements that go far beyond just reducing tics.
Table of Contents
What Are Histamines and Why Do They Matter for Tic Disorders?
Histamines are far more complex than most people realize. While you might know them as the culprits behind allergic reactions, histamines serve as crucial players in your child’s immune system, acting simultaneously as hormones, neurotransmitters, and immune mediators.
The Multiple Roles of Histamine
In your child’s body, histamines wear many hats:
- Immune System Regulation: They coordinate inflammatory responses and help fight infections
- Neurotransmitter Function: They influence brain chemistry, affecting mood, attention, and neurological function
- Digestive Support: They stimulate stomach acid production for proper digestion
- Sleep-Wake Cycles: They help regulate circadian rhythms and alertness
- Vascular Function: They control blood vessel dilation and permeability
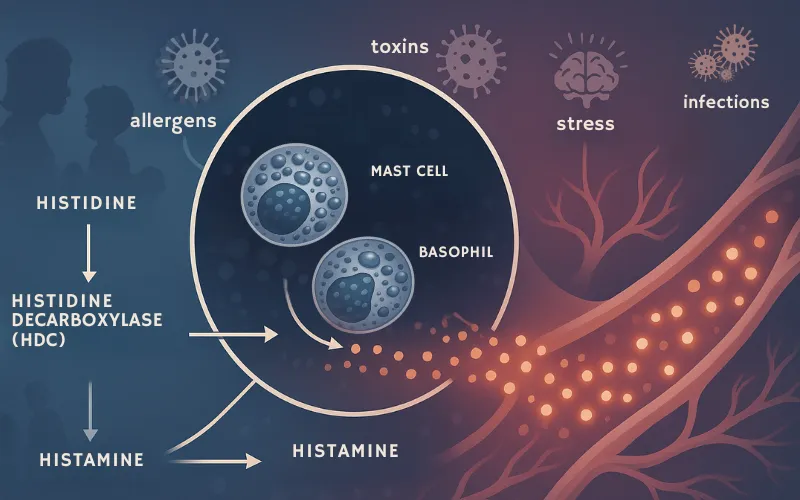
The Histamine Production Process
Histamines are created when the amino acid histidine is converted by the enzyme histidine decarboxylase (HDC). This process primarily occurs in specialized immune cells called mast cells and basophils. When these cells are triggered by allergens, infections, stress, or toxins, they release stored histamine into the bloodstream.
Recent Research on Histamine and Tic Disorders
Groundbreaking research has identified a rare mutation in the histidine decarboxylase (HDC) gene in families with high rates of Tourette syndrome and tic disorders. This discovery suggests that histamine deficiency—not just excess—can be a causal factor in tic pathophysiology.
Studies show that histamine modulates key neurotransmitter systems involved in tic disorders, including dopamine, GABA, and serotonin. When histamine signaling becomes dysregulated, particularly through the H3 receptor in the brain’s striatum, it can trigger tic-like behaviors.
The Histamine-Tic Disorder Connection: What Parents Need to Know
The relationship between histamines and tic disorders is more intricate than a simple cause-and-effect scenario. Research reveals that histamine dysregulation can both contribute to and result from the complex neuroinflammatory processes underlying tic disorders.
Understanding Histamine Dysregulation in Children
Children with tic disorders often exhibit signs of immune system dysfunction and chronic inflammation. This inflammatory state can trigger excessive histamine release from mast cells, creating a cascade of symptoms that extend far beyond visible tics:
- Increased anxiety and irritability
- Sleep disturbances and restlessness
- Digestive issues and food sensitivities
- Skin reactions and respiratory symptoms
- Cognitive difficulties and attention problems
The MCAS Connection: More Than Just Allergies
Many children with tic disorders also show signs of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS), a condition where mast cells release excessive amounts of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. However, MCAS represents just one piece of the puzzle—not the complete picture of histamine-related tic disorders.
While MCAS can contribute to tic symptoms through chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation, addressing histamine issues in tic disorders requires a more comprehensive approach that looks at the entire neuroimmune system.
The “Check Engine Light” Approach: Understanding Tics as Symptoms
I often tell parents to think of their child’s tics like a car’s check engine light. When that light comes on, you don’t just put tape over it and ignore it—you investigate what’s causing the warning signal. Tics work the same way; they’re your child’s body signaling that something deeper needs attention.
Natalia’s Transformation: A Real-World Success Story
Let me share the story of Natalia, the daughter of one of my clients, Danielle. When Natalia first came to see me, she was experiencing multiple tics that were significantly impacting her daily life and self-esteem. Her parents had been told by conventional doctors that there was nothing they could do except wait and see if the tics would resolve on their own.
Through comprehensive testing, we discovered that Natalia had several underlying issues contributing to her tic disorder:
- Severe intestinal permeability (leaky gut syndrome)
- Chronic bacterial overgrowth in her digestive system
- Candida overgrowth affecting her gut microbiome
- Exposure to environmental mold toxins
- Multiple food sensitivities triggering inflammatory responses
- Heavy metal toxicity from environmental sources
The Root Causes Behind Histamine-Related Tic Disorders
Based on my clinical experience with hundreds of children, I’ve identified the most common root causes that trigger histamine dysregulation and contribute to tic disorders:
Intestinal Permeability (Leaky Gut): When the intestinal barrier becomes compromised, undigested food particles and toxins enter the bloodstream, triggering immune responses and histamine release.
Chronic Infections: Bacterial overgrowth, parasites, and viral infections create ongoing inflammation that keeps the immune system in a hyperactive state, perpetuating a cycle of inflammation.
Fungal Overgrowth: Candida and other pathogenic yeasts produce toxins that disrupt immune function and trigger the release of histamine.
Environmental Toxins: Mold mycotoxins, heavy metals, and chemical exposures overwhelm the body’s detoxification systems and trigger inflammatory responses.
Food Sensitivities: Unlike true allergies, food sensitivities create delayed immune reactions that can trigger histamine release hours or days after consumption.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in key nutrients, such as magnesium, B vitamins, and zinc, impair the body’s ability to regulate histamine metabolism properly.
The Truth About Histamine Intolerance: Separating Fact from Fiction
One of the biggest misconceptions I encounter is the belief that most children with tic disorders have true histamine intolerance. The reality is far more nuanced and hopeful.
The 1-3% Reality
True genetic histamine intolerance—caused by inherited deficiencies in the DAO (diamine oxidase) enzyme that breaks down histamine—affects only 1-3% of the population. This means that the vast majority of children experiencing histamine-related symptoms don’t have a permanent, genetic inability to process histamine.
Beyond Simple Intolerance
Most children with histamine-related tic disorders have acquired histamine dysregulation caused by the root factors I mentioned earlier. This is incredibly important because it means their condition is often reversible when the underlying causes are addressed.
The Limitations of MCAS Diagnosis
While Mast Cell Activation Syndrome has gained attention in recent years, the diagnostic criteria are still evolving, and many children who don’t meet strict MCAS criteria still benefit from histamine-focused interventions. This is why comprehensive functional testing is so crucial.
Genetic Testing: A Piece of the Puzzle
Genetic testing can identify predispositions to histamine metabolism issues, but it doesn’t tell the whole story. Even children with genetic variants affecting DAO enzyme function can often experience significant improvement when their overall toxic burden is addressed and their body’s natural detoxification processes are supported.
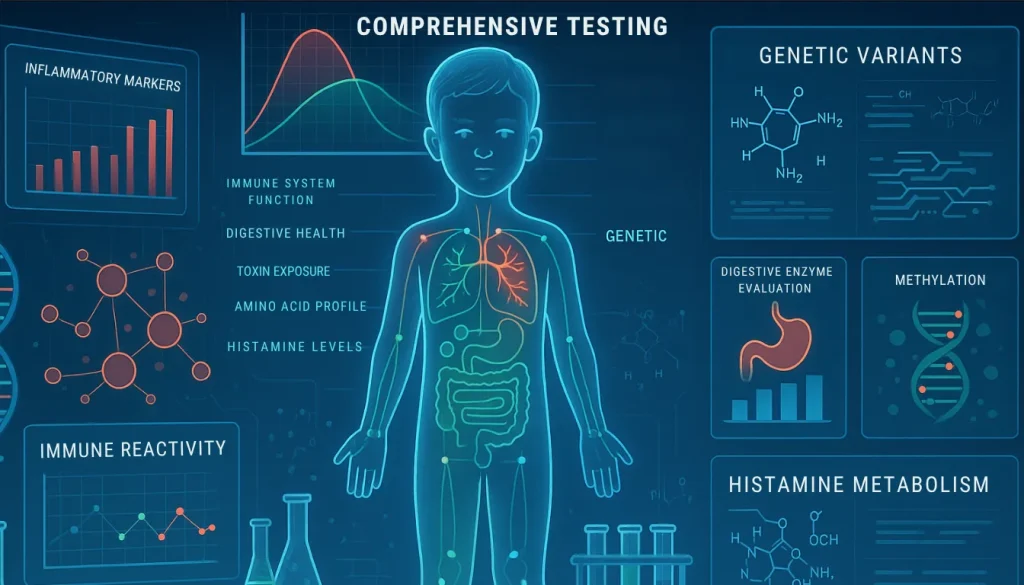
Comprehensive Testing: The 935-Biomarker Analysis Advantage
Standard medical testing often misses the complex web of factors contributing to histamine-related tic disorders. This is why conventional doctors frequently tell parents there’s “nothing wrong” with their child, despite obvious symptoms.
Why Standard Testing Falls Short
Typical medical evaluations for tic disorders usually include:
- Basic blood work checking for obvious deficiencies
- Neurological examinations
- Sometimes brain imaging studies
While these tests can rule out severe neurological conditions, they miss entirely the immune, metabolic, and environmental factors that drive most cases of childhood tic disorders.
The Power of Comprehensive Analysis
In my practice, I utilize a comprehensive 935-biomarker analysis that examines:
Immune System Function
- Inflammatory markers and cytokine levels
- Autoimmune antibodies and immune reactivity
- Mast cell activation markers
Digestive Health Assessment
- Comprehensive stool analysis for bacterial overgrowth
- Intestinal permeability testing
- Digestive enzyme function evaluation
Toxin Exposure Evaluation
- Heavy metal testing through hair and urine analysis
- Mold mycotoxin assessment
- Environmental chemical exposure markers
Nutritional Status Analysis
- Comprehensive vitamin and mineral panels
- Amino acid profiles
- Essential fatty acid levels
Histamine Metabolism Assessment
- DAO enzyme activity levels
- Histamine and methylhistamine levels
- Genetic variants affecting histamine processing
This comprehensive approach reveals the unique combination of factors contributing to each child’s tic disorder, allowing for truly personalized treatment protocols.

Functional Treatment Protocols: Addressing Root Causes for Lasting Results
Once we identify the specific factors contributing to your child’s histamine dysregulation and tic disorder, we can implement targeted interventions that address the root causes rather than just managing symptoms.
Phase 1: Stabilization and Support
The first phase focuses on stabilizing your child’s immune system and providing immediate support:
Histamine Stabilization
- Natural antihistamine compounds like quercetin and vitamin C
- DAO enzyme supplementation when indicated
- Mast cell stabilizing nutrients
Gut Barrier Support
- L-glutamine and other gut-healing nutrients
- Probiotics specifically chosen based on testing results
- Anti-inflammatory compounds to reduce intestinal inflammation
Phase 2: Pathogen Elimination
Based on testing results, we systematically address underlying infections:
Bacterial Overgrowth Treatment
- Targeted antimicrobial herbs and nutrients
- Biofilm disruption protocols
- Digestive support during treatment
Fungal Overgrowth Management
- Antifungal protocols using natural compounds
- Dietary modifications to starve pathogenic yeasts
- Immune system support during treatment
Phase 3: Detoxification and Environmental Cleanup
This phase focuses on reducing toxic burden and supporting natural detoxification:
Heavy Metal Chelation
- Gentle chelation protocols appropriate for children
- Supporting nutrients to protect during detoxification
- Monitoring to ensure safe and effective treatment
Mold and Environmental Toxin Elimination
- Binders to remove mycotoxins and other environmental toxins
- Liver and kidney support during detoxification
- Environmental assessment and remediation guidance
Phase 4: Nutritional Optimization and Long-term Support
The final phase ensures your child has all the nutrients needed for optimal neurological and immune function:
Targeted Nutrient Therapy
- Individualized supplementation based on testing results
- Focus on nutrients crucial for neurotransmitter production
- Support for methylation and detoxification pathways
Dietary Optimization
- Elimination of trigger foods identified through testing
- Anti-inflammatory dietary protocols
- Nutrient-dense meal planning guidance
Prevention and Long-Term Management: Maintaining Your Child’s Progress
Successfully addressing histamine-related tic disorders isn’t just about initial treatment—it’s about creating sustainable lifestyle changes that support your child’s long-term health and prevent symptom recurrence.
Dietary Modifications for Histamine Balance
While true histamine intolerance is rare, many children benefit from temporary dietary modifications during the healing process:
Foods to Minimize During Treatment
- Aged and fermented foods (cheese, wine, sauerkraut)
- Processed meats and foods with preservatives
- Citrus fruits and tomatoes during the acute phases
- Foods high in artificial additives and colorings
Healing Foods to Emphasize
- Fresh, organic vegetables and fruits
- High-quality proteins from grass-fed and wild-caught sources
- Anti-inflammatory fats like olive oil and avocados
- Bone broth and other gut-healing foods
DAO Enzyme Support Strategies
For children with reduced DAO enzyme activity, specific support strategies can be helpful:
- DAO enzyme supplementation with meals when indicated
- Supporting nutrients like vitamin B6, vitamin C, and copper
- Avoiding medications and substances that inhibit DAO activity
- Timing meals to optimize histamine clearance
Environmental Factors and Lifestyle Modifications
Creating a low-toxin environment supports your child’s ongoing recovery:
Home Environment Optimization
- Air purification systems to reduce airborne toxins
- Water filtration to remove chlorine and other chemicals
- Non-toxic cleaning and personal care products
- Mold prevention and remediation when necessary
Stress Management and Sleep Optimization
- Regular sleep schedules to support circadian rhythm balance
- Stress reduction techniques appropriate for children
- Physical activity to support natural detoxification
- Mindfulness and relaxation practices
Conclusion and Next Steps: Hope for Your Child’s Future
The connection between tic disorders and histamines represents a paradigm shift in how we understand and treat these challenging conditions. Rather than accepting tics as permanent neurological quirks, we can now address the underlying immune and metabolic imbalances that drive them.
Your child’s tics are not a life sentence—they’re a signal that their body needs support. By identifying and addressing the root causes of histamine dysregulation, we can help your child not only reduce their tics but also improve their overall health, energy, and quality of life.
The healing journey requires patience, comprehensive testing, and individualized treatment protocols. But the results speak for themselves: children like Natalia who have transformed from struggling with debilitating tics to thriving, healthy kids who can focus on being children again.
If you’re ready to move beyond the “wait and see” approach and discover what’s driving your child’s tic disorder, I invite you to schedule a comprehensive consultation. Together, we can uncover the unique factors contributing to your child’s symptoms and create a personalized healing plan that addresses the root causes for lasting results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tic Disorders and Histamines
While true genetic histamine intolerance affects only 1-3% of the population, histamine dysregulation can definitely contribute to tic disorders in children. Research has identified mutations in histamine-producing genes in families with high rates of Tourette syndrome, and histamine imbalances can trigger neuroinflammatory processes that manifest as tics. However, most children with histamine-related tics have acquired dysregulation due to underlying infections, toxin exposure, or gut dysfunction rather than true genetic intolerance.
Foods that can trigger histamine release or contain high levels of histamine include aged cheeses, fermented foods, processed meats, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and foods with artificial preservatives. However, it’s important to note that food triggers are highly individual. Rather than following generic histamine-elimination diets, comprehensive testing can identify your child’s specific food sensitivities and triggers, allowing for a more targeted and effective dietary approach.
Comprehensive testing for histamine-related tic disorders goes far beyond standard medical tests. A thorough evaluation should include assessments of histamine and methylhistamine levels, DAO enzyme activity, comprehensive stool analysis for gut dysfunction, mold and mycotoxin testing, heavy metal analysis, food sensitivity panels, and inflammatory markers. This 935-biomarker approach reveals the complex web of factors contributing to histamine dysregulation and tic symptoms.
No, MCAS and histamine intolerance are different conditions, though they can overlap. MCAS involves the excessive activation of mast cells, which release histamine and other inflammatory mediators. In contrast, histamine intolerance typically refers to a reduced ability to break down dietary histamine due to a deficiency in the DAO enzyme. Many children with tic disorders show signs of mast cell activation without meeting strict MCAS diagnostic criteria, which is why a comprehensive functional medicine evaluation is crucial.
Treatment timelines vary significantly based on the underlying root causes and the child’s healing capacity. Some children experience improvements within weeks of starting treatment, while others may require 6 to 12 months for significant changes. Factors affecting the timeline include the severity of gut dysfunction, toxic burden, presence of chronic infections, and compliance with treatment protocols. The key is addressing root causes systematically rather than expecting quick fixes.
While “cure” is a strong word, many children experience dramatic improvements in their tic symptoms when underlying histamine dysregulation and root causes are appropriately addressed. Success depends on identifying and treating all contributing factors, not just histamine imbalances. Children like Natalia have achieved remarkable transformations, but each case is unique and requires individualized assessment and treatment protocols.
Allergies involve immediate IgE-mediated immune responses that typically occur within minutes.
If you are ready to dig deeper into your child’s tic disorder, click here and start with the Tic Disorder Cheat Sheet.
References
Ercan-Sencicek, A., Stillman, A., Ghosh, A., Bilguvar, K., O’Roak, B., Mason, C., Abbott, T., Gupta, A., King, R., Pauls, D., Tischfield, J., Heiman, G., Singer, H., Gilbert, D., Hoekstra, P., Morgan, T., Loring, E., Yasuno, K., Fernandez, T., Sanders, S., Louvi, A., Cho, J., Mane, S., Colangelo, C., Biederer, T., Lifton, R., Gunel, M., & State, M. (2010). L-histidine decarboxylase and Tourette’s syndrome.. The New England journal of medicine, 362 20, 1901-8 . https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0907006.